Semiconductor
Semiconductor Introduction
Semiconductor (semiconductor) refers to a material whose conductivity is between a conductor and an insulator at room temperature.
Semiconductors are used in integrated circuits, consumer electronics, communication systems, photovoltaic power generation, lighting, high-power power conversion and other fields. For example, diodes are devices made of semiconductors.
Whether from the perspective of technology or economic development, the importance of semiconductors is very huge. Most electronic products, such as computers, mobile phones or digital recorders, are closely related to semiconductors.
Common semiconductor materials are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc., and silicon is the most influential one in various semiconductor materials applications.
First Generation Semiconductor
Mainly refers to silicon (Si), germanium (Ge) as the representative of the element semiconductor materials, the application is very common, including integrated circuits, electronic information network engineering, computers, mobile phones and so on. Among them, the most typical application is integrated circuits, which are mainly used in low-voltage, low-frequency, low-power transistors and detectors, replacing bulky electronic tubes, leading to the possibility of integrated circuits.
Second generation semiconductor
It is mainly a compound material represented by gallium arsenide (GaAs) and indium phosphide (InP), which is mainly used in millimeter wave devices and light-emitting devices. Satellite communication, mobile communication, optical communication, GPS navigation, etc. It has good electron mobility, band gap and other material properties, scarce resources, toxic, polluting the environment.
Third-generation semiconductors
Refers to silicon carbide (SiC), gallium nitride (GaN), zinc oxide (ZnO), diamond, aluminum nitride (AlN) as the representative of broadband semiconductor materials, with better electron mobility, band gap, breakdown voltage, high temperature, high frequency, anti radiation, high power devices and other characteristics. Most of them are used in communications, new energy vehicles, high-speed rail, satellite communications, aerospace and other scenarios, among which the research and development of silicon carbide and gallium nitride are more mature.
Semiconductor wafer production process flow
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Yuhuan can be used as process section
|
Silicon, Silicon Carbide, Sapphire Wafers-Post-Cut Grinding |
Silicon, Silicon Carbide, Sapphire Wafers-Single-sided coarse and fine polishing |
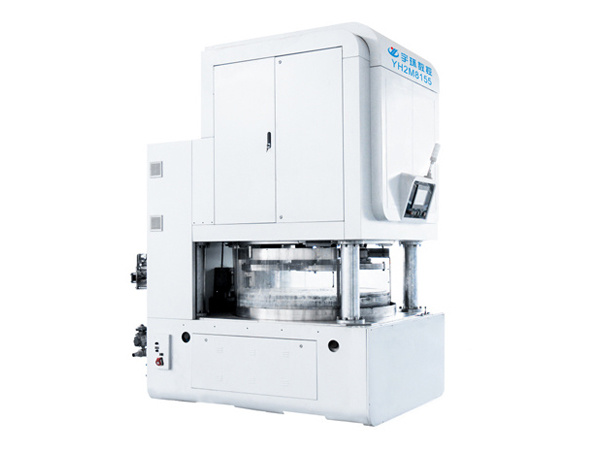
Applicable equipment of Yuhuan
Main process:
CMP(Chemical Mechanical Polishing,化学机械抛光)
Rough polishing: generally use magnesium oxide for rough polishing, the purpose is to remove the residual mechanical damage on the surface of the silicon wafer, and it is generally required to remove 20 ~ 30μm from the surface.
Fine polishing: fine polishing with silicon dioxide, the purpose of which is to remove the slight damage and cloud-like defects left on the surface of the silicon wafer by the first polishing, and it is required to remove a thickness of 2 to 3 μm from the surface.







